The digital world is constantly evolving with new technologies, frameworks and standards emerging every day.
These innovations make it possible to tackle complex requirements efficiently.
A web development framework is one such innovation in the development field, which revolutionised programming by providing pre-built foundations for applications.
It has eliminated the need for developers to code from scratch, reducing development time and improving efficiency.
With a number of web development frameworks available in the industry, knowing the different types and their features is essential for developers to choose the right framework for their projects.
After reading this article, you will gain a complete understanding of web development frameworks. So, let’s get started.
What is a Web Development Framework
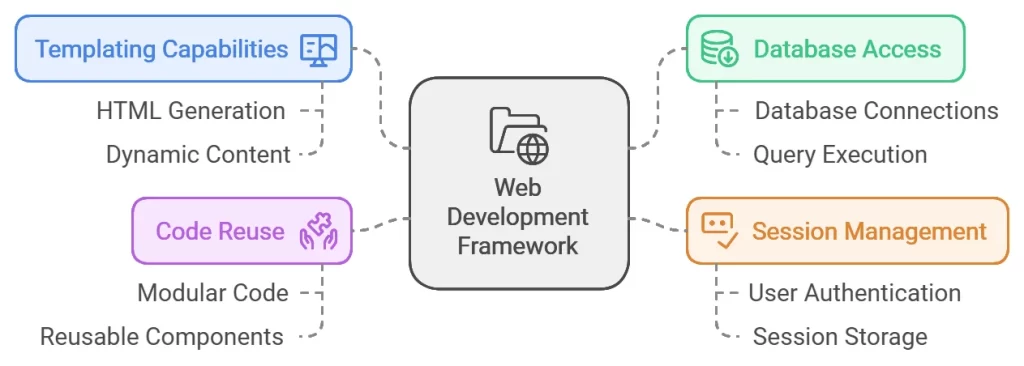
A web framework is a software framework that is developed to simplify the process of building websites and web applications.
It is the standard way to build and deploy web applications on the internet.
The main aim of web development frameworks is to automate common activities performed during the development phase.
These frameworks come with templating capabilities, libraries for database access, session management, and code-reuse features that help speed development.
These frameworks are available in several programming languages.
Top 5 Benefits of Using Web Frameworks
Unlike other development tools, frameworks come with a predefined codebase and guidelines for easier website development. As a result, they speed up the development process and thereby reduce time-to-market.
Here are the top 5 benefits of using web frameworks:
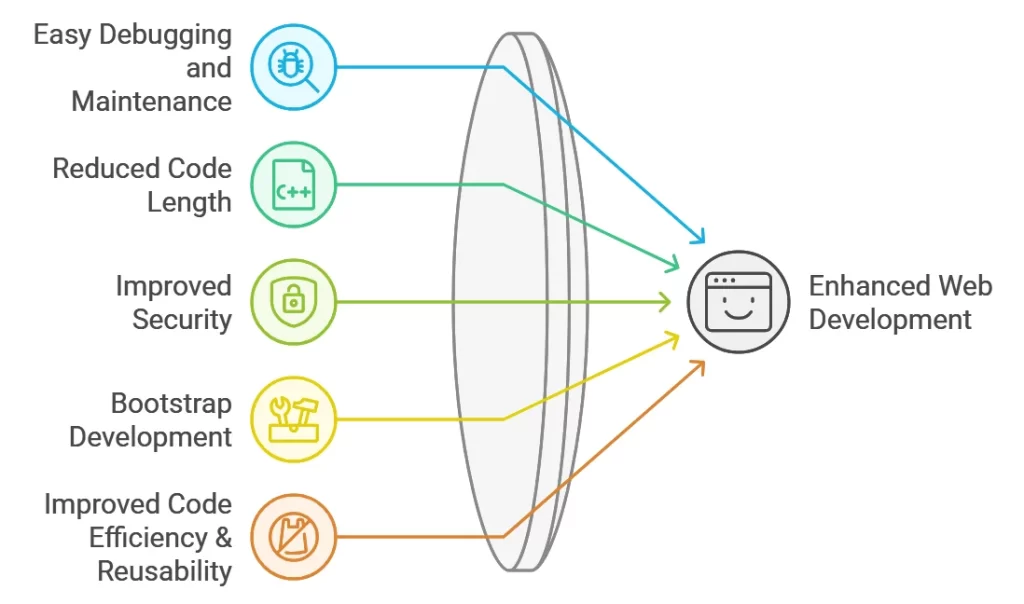
1. Easy Debugging and Maintenance
Most programming languages don’t prioritise code readability and maintainability.
However, many popular web development frameworks do.
Frameworks are recommended for custom web development because they simplify debugging and maintenance.
Most frameworks have active developer communities that provide quick support for common issues.
2. Reduce Code Length
When you use frameworks, you don’t need to write long blocks of code to add standard functionality to a website.
Frameworks come with code-generation features to promote simplicity and conciseness, reducing the time and effort required by developers.
Moreover, frameworks provide tools and functions that help developers automate regular tasks like authentication, URL mapping, caching, etc.
3. Improved Security
Frameworks provide built-in security features and mechanisms that help developers protect applications from common security threats.
By using frameworks, programmers can safeguard websites from various cyberattacks like data tampering, DDoS attacks, SQL injection, etc.
Moreover, you can use open-source web frameworks to build custom security specifications for websites.
4. Bootstrap Development
Frameworks offer a variety of tools and packages to help developers bootstrap the development process.
By using frameworks, programmers do not have to write all scripts from scratch.
For developers with less experience, frameworks provide tools and conventions that help explore specific features more easily, similar to how an experienced developer would.
Moreover, frameworks handle many routine development tasks from the start and significantly reduce coding time.
5. Improves Code Efficiency & Reusability
Web frameworks provide a fast, responsive, and efficient development environment for developers.
In addition, frameworks come with advanced features like hot reload and live reload, leading to faster development cycles.
Developers rarely need to write complex or repetitive code when using frameworks.
Instead, they can use a predefined codebase to make modifications and bootstrap projects quickly.
Classification of Framework Architectures
Framework architecture determines the relation between different elements of a framework.
The type of framework architecture plays a large role in the application’s functioning.
Framework architectures can be classified into:
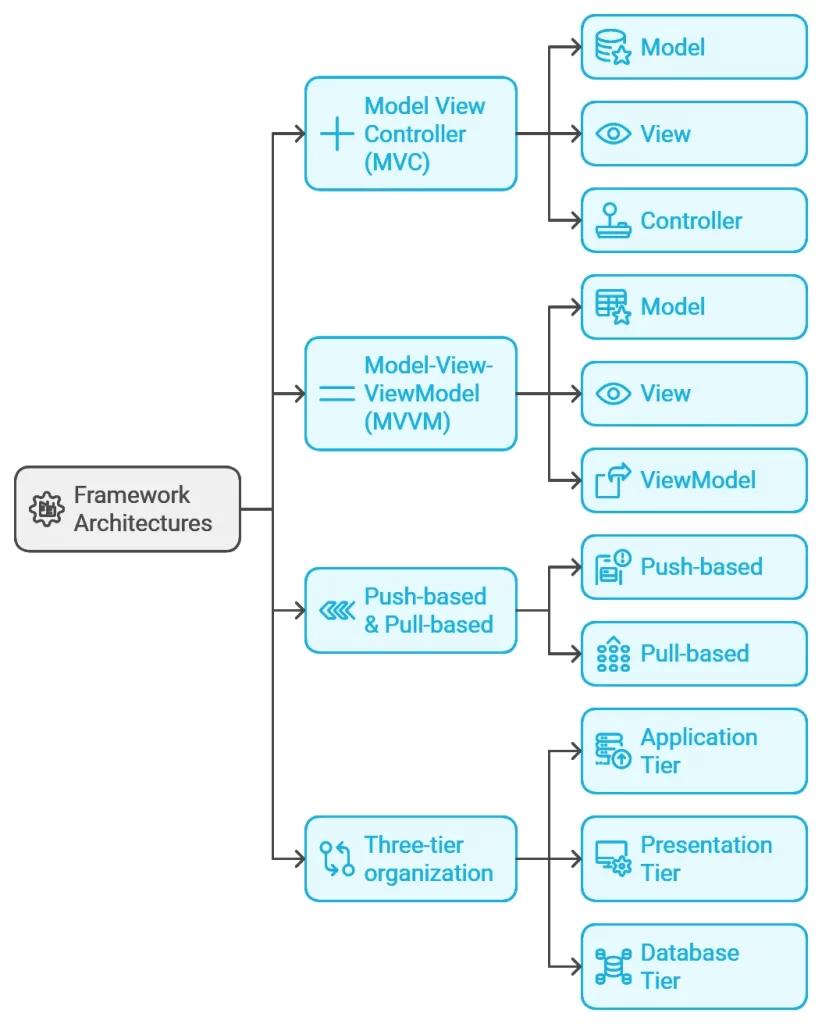
1. Model View Controller (MVC)
MVC, or Model-View-Controller, is a popular architectural pattern used by many frameworks.
In the MVC model, the application is divided into three main components — the Model, the View, and the Controller.
Each component handles specific functions. This separation makes complex application development simpler and more manageable.
2. Model-View-ViewModel (MVVM)
MVVM allows for clean and organized structuring of code according to design patterns.
Here, the presentation logic is separated from the core business logic.
The different layers in MVVM are Model, View, and ViewModel.
3. Push-based & Pull-based
Push-based architectures are action-driven, while pull-based architectures are component-driven.
Push-based models start with an action and then push the data to the view layer.
Pull-based architectures, on the other hand, start with the view layer and pull the required data/components.
4. Three-tier organization
Commonly used for client-server applications, three-tier architecture separates applications into three logical and physical tiers.
The three tiers are the presentation tier, application (business) tier, and database tier.
Framework vs. Libraries
When learning web development, you’ll often hear the terms “framework” and “library” — and they are not the same.
|
Library |
Framework |
|
A library is a collection of pre-written code that you can call and use whenever you need. |
A framework is a bigger structure that provides a skeleton for your entire application |
|
You stay in control: You decide when and how to use the library. |
It stays in control: Your code fits into its structure and the framework calls your code when needed. |
Example: React (UI library), jQuery, D3.js . |
Example: Angular, Django, Laravel, Next.js. |
|
Using a library is like picking tools from a toolbox whenever you need them. |
Using a framework is like following a construction blueprint that tells you where every tool and material goes. |
Different Types of Web Development Frameworks
Web development frameworks can be classified based on the programming language they are written in and their use cases.
Express, for example, is used with Node.js; Ruby on Rails is written in Ruby; and Django is written in Python.
According to their use cases, Angular and React are meant for front-end development, and Django is commonly used for back-end development.
There are also frameworks designed to solve very specific problems, such as database connections and security administration.
Now, let’s discuss front-end frameworks, back-end frameworks, and full-stack frameworks separately.
1. Full-Stack frameworks
Full-stack frameworks provide tools and conventions for building both the front end and the back end of an application within a single ecosystem. They often include routing, data fetching, server-side rendering or hydration, API endpoints, and opinionated project structure.
Examples include Next.js, Nuxt.js, Remix, RedwoodJS, Meteor.js, and SvelteKit.
2. Frontend frameworks
Front-end frameworks are designed to create user interface elements to simplify the development process.
These frameworks provide pre-written, reusable components, tools for styling, form validation, and more.
Some front-end frameworks also help optimize SEO and improve your website’s loading time.
Front-end frameworks are primarily based on HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Some popular examples are React, Vue.js, Angular, Svelte, and Preact.
Note: React is technically a JavaScript library, not a framework, but it is often grouped with frontend frameworks because of how it is used to build entire user interfaces. Similarly, Tailwind CSS and Bootstrap are CSS frameworks focused only on styling, not full web app structure.
3. Backend frameworks
Back-end frameworks help you develop the server-side of your website quickly and efficiently.
These frameworks are used for user authentication, setting up secure connections, and connecting with databases.
Different frameworks are used for different languages to develop the server, such as Express for Node.js, Django for Python, Ruby on Rails for Ruby, and Laravel for PHP.
You have many options to choose from in terms of both programming languages and frameworks.
Frontend vs Backend vs Full-Stack Web Frameworks
Frameworks are web development tools specially built to make the web development process faster and more secure.
But, depending on their use cases, frameworks can be categorized into three Front-end frameworks, back-end frameworks and full stack frameworks
|
Front-end Framework |
Back-end Framework |
Full-stack Framework |
|
A front-end framework is used to develop the user interface of a website or application — the part a user sees and interacts with. |
A back-end framework is a library of tools and modules that aid in the development of a website’s server-side architecture. It handles server-side functions. |
A full-stack framework covers both frontend and backend within one ecosystem, letting developers build end-to-end apps without switching between tools. |
|
Front-end frameworks provide pre-written components and templates that can be reused across the UI. |
Back-end frameworks are used for user authentication, database manipulation, session handling, URL routing, and security management. |
Full-stack frameworks handle routing, data fetching, server-side rendering, API endpoints, and may include built-in database layers. |
|
Front-end frameworks help create SEO-optimized, mobile-friendly websites with responsive components used for building UI. |
The primary purpose of using back-end frameworks is URL routing, storing user-generated data, managing authentication, and ensuring security. |
Full-stack frameworks offer a single workflow for building both sides of the app, which saves time and reduces complexity. |
|
Popular front-end examples: React, Vue.js, Angular, Svelte, Preact. |
Popular back-end examples: Django, Express.js, Ruby on Rails, .NET, Laravel, NestJS. |
Popular full-stack examples: Next.js, Nuxt.js, Remix, RedwoodJS, Meteor.js, SvelteKit. |
|
The most widely used front-end language is JavaScript, while HTML and CSS are used for markup and styling respectively. |
Some of the most widely used back-end languages are Node.js (JavaScript), Python, Ruby, and PHP. |
Full-stack frameworks typically use JavaScript (Node.js + React/Vue/Svelte) or a combination of back-end and front-end languages, allowing developers to build entire applications with a single, unified tech stack. |
17 Best Frontend Web Development Frameworks and Key Features
Front-end is the most visible layer of any website. It is where user experience is forged, and where the visual design and interactive elements of a site come to life. For any digital agency or web design company in Dubai, the selection of a front-end framework is paramount to creating the compelling, high-performance applications clients demand. The following list details 17 of the most popular front-end frameworks and libraries shaping web development in 2026. Each offers a distinct approach to building responsive, dynamic, and intuitive user interfaces.
1. Angular
A powerful, opinionated, and full-fledged framework for building complex single-page applications. It’s developed and maintained by Google. It enforces a structured approach to development, making it a good choice for large-scale, enterprise applications.

Key Features
-
TypeScript-based: Provides static typing and improved tooling.
-
Dependency Injection: A core concept for managing components and services.
-
Component-based Architecture: Applications are built from reusable components.
-
CLI (Command Line Interface): Simplifies development tasks like scaffolding and building.
2. React
A JavaScript library for building user interfaces, often used as a framework. Developed and maintained by Meta, it excels at building dynamic UIs with a declarative, component-based approach. It’s highly popular and has a vast ecosystem.

Key Features
- Virtual DOM: Improves performance by minimizing direct DOM manipulations.
- Component-based: Builds UIs with encapsulated, reusable components.
-
JSX: A syntax extension that allows writing HTML-like code within JavaScript.
-
Declarative Views: Simply describe the UI for a given state, and React handles the updates.
3. Vue.js
A progressive framework known for its simplicity and ease of use. It’s highly approachable for beginners and can be integrated into existing projects incrementally. Vue offers an elegant and efficient way to build both simple and complex UIs.

Key Features
- Lightweight: Has a small file size, leading to fast loading times.
-
Single-File Components: Encapsulates HTML, CSS, and JavaScript in a single .vue file.
-
Reactive Data Binding: Automatically updates the view when the data model changes.
-
Official CLI: Provides a robust tool for project scaffolding and management.
4. Ember.js
An opinionated framework that focuses on “convention over configuration,” providing a full development stack out-of-the-box. It’s perfect for building large, ambitious single-page applications and is known for its stability and developer productivity.

Key Features
-
Ember CLI: A powerful command-line tool for scaffolding and project management
-
Convention over Configuration: Reduces the amount of decisions developers need to make.
-
Integrated Data Layer (Ember Data): Simplifies data fetching and management.
-
Extensive Router: Provides powerful URL management for complex applications.
5. Backbone.js
A minimalist JavaScript library that provides a structure for web applications with a Model-View-Presenter (MVP) pattern. It gives developers maximum freedom and is perfect for building lightweight and flexible client-side applications.

Key Features
- Models and Collections: Organizes data with key-value binding and custom events.
- Views and Events: Handles UI rendering and user interactions.
- Routers: Manages application state through URL navigation.
- Lightweight and Flexible: Provides structure without being overly opinionated
6. Svelte
A radical new approach to building web applications. Svelte is a compiler that turns your components into small, vanilla JavaScript bundles at build time, rather than interpreting a framework at runtime. This results in incredibly fast apps.

Key Features
-
No Virtual DOM: Achieves better performance by directly updating the DOM.
-
Reactive by Default: State changes automatically trigger updates without boilerplate code.
-
Small Bundle Size: Compiles to highly optimized, tiny bundles.
-
Built-in Transitions: Includes a simple API for creating smooth animations
7. Preact
A fast and lightweight alternative to React with a nearly identical API. It’s a great choice for projects where performance and bundle size are critical, as it provides most of React’s features in a much smaller package.

Key Features
- Small Size: Extremely lightweight, at around 3.5 kB.
- React Compatibility: Offers a familiar API and can be used with many React libraries.
- Performance: Faster rendering and efficient memory usage.
- Efficient: Focuses on performance by avoiding complex features.
8. Lit
A simple library for building fast, lightweight, and standards-compliant web components. It provides a foundational layer for creating custom HTML elements that are highly performant and can be used in any modern web environment, regardless of the framework

Key Features
- Web Components Standard: Adheres to the browser’s native component model.
- Reactive Properties: Automatically updates the component when a property changes.
- Small Footprint: Tiny and performant, contributing to fast load times.
- Template Literals: Uses tagged template literals for creating and rendering components.
9. Solidjs
A reactive JavaScript library for building user interfaces that’s known for its high performance. Unlike frameworks that use a virtual DOM, SolidJS compiles JSX into real DOM nodes and fine-grained reactive updates, resulting in exceptionally fast performance.

Key Features
- Fine-Grained Reactivity: Updates the UI with surgical precision, only re-rendering what’s changed.
- No Virtual DOM: Compiles to performant, native JavaScript code.
- JSX Syntax: Uses a familiar JSX syntax similar to React.
10. Alpine.js
A minimal, lightweight framework for adding declarative and reactive behavior directly to your HTML. It’s ideal for adding simple interactivity to static sites or for small-to-medium-sized projects without the overhead of a full-scale framework.

Key Features
- Minimalistic: Extremely small footprint.
- In-HTML Directives: Logic is written directly in the HTML markup.
- No Build Step Required: Can be included with a simple script tag.
- Vue.js-inspired Syntax: Easy to learn for developers familiar with Vue
11. JQuery
A fast, small, and feature-rich JavaScript library. It simplifies HTML DOM traversal and manipulation, event handling, animation, and Ajax. While not a framework, its widespread use makes it a foundational tool for front-end development.

Key Features
-
DOM Manipulation: Simplifies selecting and manipulating HTML elements.
-
Event Handling: Provides an intuitive way to manage user interaction
- AJAX: Makes asynchronous data requests easy to implement.
-
Cross-Browser Compatibility: Handles inconsistencies between browsers
12. Semantic UI
A development framework that helps create beautiful, responsive layouts using human-friendly HTML. It uses natural language principles to create intuitive and easy-to-read class names, making component styling a breeze.

Key Features
- Human-Friendly HTML: Uses classes like ui labeled icon button that are easy to understand.
-
Theming: A robust theming system allows for complete design freedom.
- Simplified Debugging: Provides logging to track down performance bottlenecks.
-
Rich UI Components Offers a wide range of well-designed components.
13. Foundation
An advanced, responsive front-end framework that is highly flexible and customizable. It is a solid choice for building complex, professional websites and applications that require a strong, semantic HTML structure.

Key Features
-
Semantic HTML: Encourages the use of meaningful HTML tags.
-
Mobile-First: Designed with a mobile-first approach for all screen sizes
- Modular: You can choose to include only the components you need
- Advanced Features: Includes powerful components like off-canvas menus and a flexible grid.
14. Materialise
A modern responsive front-end framework based on Google’s Material Design. It offers a standardized and visually appealing design language with a wide array of ready-to-use components and a simple-to-learn structure

Key Features
-
Material Design Principles: Adheres to Google’s design system for a consistent look and feel.
-
Ready-to-Use Components: Includes pre-built components like cards, buttons, and navbars
- Responsive: Built with a responsive grid system that adapts to all devices.
- Easy to Learn: Simple to get started and integrate into projects.
15. Knockout.js
A JavaScript library that uses the Model-View-ViewModel (MVVM) pattern to simplify dynamic user interfaces with data binding. It allows you to automatically update your UI when your data model changes, a concept known as “declarative bindings.
Key Features
-
Declarative Bindings: Connects UI elements to the data model using a simple syntax.
-
Dependency Tracking: Automatically detects dependencies and updates the UI.
-
Templating: Allows for reusable UI components.
- Extensible: Can be customized with a plugin framework
16. Tailwind CSS
A utility-first CSS framework for rapidly building custom designs directly in your HTML. Instead of providing pre-made components, it gives you a library of low-level utility classes that you can combine to build unique user interfaces.
Key Features
-
Utility-First: Uses single-purpose classes (e.g., flex, pt-4, text-center) for styling.
-
Highly Customizable: You can configure everything, from colors to spacing, in a tailwind.config.js file.
-
PurgeCSS: Automatically removes unused CSS, leading to small production file sizes.
- Responsive by Default: Uses prefixes for mobile-first responsive design.
17. Bootstrap
The most popular CSS framework for building responsive, mobile-first websites. It provides a comprehensive set of pre-styled components, a flexible grid system, and JavaScript plugins to accelerate development and ensure consistency across projects.

Key Features
-
Responsive Grid System: A 12-column grid for creating responsive layouts.
-
Pre-designed Components: Includes a vast library of UI components (e.g., buttons, forms, modals).
-
Sass Variables: Allows for easy customization of colors, fonts, and spacing.
-
JavaScript Plugins: Offers optional functionality for components like carousels and tooltips.
14 Best Backend Web Development Frameworks and Key Features
If the front end is the face of an application, the back end is its powerful brain. It’s the engine that handles business logic, database interactions, security, and data management. For a web development company in Dubai, selecting a robust back-end framework is critical for building scalable, secure, and high-performance applications that can handle complex operations and user traffic. The following list details 14 of the most influential back-end frameworks that are shaping web development in 2026. Each offers a unique approach to managing server-side logic and ensuring the seamless flow of data.
1. Express.js
A minimal and flexible framework for Node.js that serves as a solid base for creating APIs and web apps. Its unopinionated design gives developers the freedom to structure applications as they see fit, using middleware to build everything from simple prototypes to complex systems.

Key Features
- Routing: Handles incoming requests and maps them to the correct endpoints.
- Middleware: Runs code, modifies requests/responses, or ends the cycle at any point.
- High Performance: Runs on top of Node.js, making it efficient for I/O-heavy workloads.
- Unopinionated: Lets developers choose their tools, libraries, and architecture
2.Django
A powerful, high-level Python framework built for rapid development and clean, pragmatic design. Following its “batteries-included” philosophy, it provides most of the tools developers need right out of the box.

Key Features
- ORM: Lets developers interact with databases using Python objects rather than raw SQL.
- Admin Interface: Auto-generates a professional, ready-to-use admin dashboard.
- Security: Protects against threats like SQL injection, CSRF, and XSS by default.
- Authentication: Includes a robust user authentication and permission system.
3.Ruby on Rails
A mature open-source framework for Ruby focused on productivity and clean code. Its “convention over configuration” approach helps developers get apps running quickly without excessive setup.

Key Features
- MVC Pattern: Separates concerns into Model, View, and Controller layers.
- Active Record: Streamlines database operations through an intuitive ORM
- DRY Principle: Encourages code reuse to minimize duplication.
- Scaffolding: Generates starter code for new features automatically.
4.Laravel
One of the most popular PHP frameworks, known for its expressive syntax and developer-first approach. Laravel comes with a powerful ecosystem and a variety of tools to build robust applications with less effort.

Key Features
- Artisan CLI: A command-line tool that speeds up routine development tasks
- Eloquent ORM: Simplifies database queries with a fluent, object-oriented syntax.
- Blade Templates: Lightweight templating engine for building dynamic views
- Authentication: Comes with built-in support for user login and security
5.Spring & Spring Boot
Spring is a comprehensive framework for Java development, ideal for enterprise-grade applications. Spring Boot builds on top of Spring to remove boilerplate setup, allowing faster, production-ready deployment.

Key Features
- Dependency Injection: Manages relationships between components for cleaner, testable code.
- Auto-Configuration: Spring Boot detects dependencies and configures them automatically.
- Embedded Servers: Runs as an executable JAR with an embedded server like Tomcat.
- Modular Design: Use only the modules you need, keeping projects lightweight.
6.Koa
Created by the team behind Express, Koa is a modern Node.js framework designed to be smaller and more expressive. It uses async/await for cleaner asynchronous code and gives developers complete control over middleware flow.

Key Features
- Async/Await: Improves readability and avoids callback hell.
- Minimal Core: Provides just the essentials, letting you build your own middleware stack.
- Cascading Middleware: Control passes down and back up the stack for flexibility.
- Context Object: Combines request and response into a single, convenient object.
7.Nest.JS
A progressive Node.js framework built with TypeScript and influenced by Angular’s architecture. It provides a structured and modular approach to building scalable, maintainable applications

Key Features
- TypeScript First: Offers strong typing for safer, cleaner code.
- Modular Design: Breaks applications into manageable, reusable modules.
- Dependency Injection: Simplifies service and component management.
- Robust Ecosystem: Strong support for testing and integration with other libraries
8.Flask
A simple and flexible Python micro-framework perfect for small to medium apps. Unlike Django, Flask keeps things minimal, letting you plug in only the extensions you need for databases, security, and more.

Key Features
- Minimal & Easy: Lightweight and beginner-friendly.
- Customizable: Freedom to choose third-party libraries and components.
- Jinja2 Templates: Dynamic HTML rendering with a powerful template engine.
- Extensions: Add ORMs, form handling, and security features as needed.
9.Phoenix
Built with Elixir and powered by the Erlang VM, Phoenix excels at building high-performance, fault-tolerant, and real-time applications that handle thousands of connections simultaneously

Key Features
- Real-time Support: WebSockets and Channels for instant updates.
- Concurrency: Handles massive parallel requests effortlessly.
- LiveView: Builds reactive user interfaces without heavy JavaScript.
- Speed: Optimized for low-latency and high throughput.
10.CakePHP
A rapid development PHP framework following the MVC design pattern. It offers a clean structure, built-in components, and conventions that speed up the development cycle.

Key Features
- MVC Pattern: Clear separation of logic, data, and UI.
- Scaffolding: Auto-generates code for new parts of the application.
- ORM: Simplifies database operations with an integrated ORM
- Security Tools: Protects against CSRF, XSS, and other threats
11.Meteor.js
A full-stack JavaScript platform designed for real-time applications, allowing changes in the database to instantly sync with connected clients—no manual refresh needed.
Key Features
- Reactive Data: Updates the UI automatically when the database changes.
- Single Language: JavaScript across both front end and back end.
- Isomorphic Code: Shared code between client and server
- Hot Code Reload: Pushes updates to users without full reloads.
12.Hapi
Hapi is a free web development framework for Node.js that may be used to create applications, APIs, and services.
Hapi.js is a rich Node.js framework designed for building scalable APIs and powerful applications with a focus on configuration over code.
Key Features
- Config-driven: Uses configuration files to define routes and logic.
- Plugin-based: Encourages modular design with reusable plugins.
- Validation Tools: Built-in request validation for safer applications.
- Scalable: Designed for enterprise-grade workloads and traffic.
13.Play
A stateless, reactive web framework for Java and Scala, ideal for building high-performance applications with asynchronous processing and smooth scalability.

Key Features:
- Stateless Design: Easy to scale horizontally.
- Async I/O: Handles heavy loads with non-blocking operations.
- Hot Reload: See code changes instantly during development.
- MVC Pattern: Follows the familiar Model-View-Controller structure
14.CodeIgniter
A fast, lightweight PHP framework with a small footprint and an easy learning curve. It’s a great choice for developers who want speed, simplicity, and direct control over their applications.

Key Features
- Lightweight: Extremely fast with minimal overhead.
- MVC Support: Separates business logic from presentation.
- Great Documentation: Clear and detailed guides for quick learning
- Rich Libraries: Includes ready-to-use tools for sessions, email, and databases.
10 Popular Full-Stack Web Frameworks
Having explored the individual strengths of front-end and back-end frameworks, we now turn to the game-changers: full-stack frameworks. These all-in-one solutions empower developers to build and manage both the user interface and the server-side logic within a single, cohesive environment. This integrated approach is especially valuable for businesses requiring robust online stores, making full-stack frameworks a top choice for any provider of ecommerce development services in Dubai.
The following list showcases 10 of the most powerful full-stack frameworks and tech stacks to consider in 2026. They are ideal for building everything from rapid prototypes to complex, scalable applications with a unified code base.
1.Next.js
Next.js is a powerful, production-ready React framework for building fast, SEO-friendly web applications. Developed by Vercel, it enables both server-side rendering and static site generation, providing a performant, hybrid approach to web development. It’s a top choice for modern, scalable, and dynamic websites.

Key Features
- Server-Side Rendering (SSR) & Static Site Generation (SSG): Pre-renders pages on the server for speed and SEO
- File-Based Routing: Creates routes automatically based on your file structure
- API Routes: Allows you to build your backend API within the same Next.js project.
2.Nuxt.js
Nuxt.js is a full-stack framework built on Vue.js, designed to simplify building universal applications. Like Next.js, it prioritizes performance with features like server-side rendering and static site generation. It has a convention-over-configuration philosophy, making it easy to get started with Vue.js projects.

Key Features
- Universal & Static Apps: Supports both SSR and SSG for flexible deployment options.
- File-Based Routing: Automatically generates routes from the pages directory.
- Auto Code Splitting: Optimizes app performance by splitting code into smaller chunks for each route.
3.Remix
Remix is a React-based framework that focuses on modern web standards to create fast and resilient user experiences. It emphasizes server-side data fetching and form submissions without excessive JavaScript, making it highly performant. Its nested routing system simplifies the management of complex UI layouts.

Key features
- Web Standards Focused: Leverages browser fundamentals for enhanced performance and reliability.
- Nested Routing: Allows for a hierarchical URL structure that mirrors the component tree.
- Automatic Error Handling & Loading States: Provides built-in mechanisms to handle errors and loading states gracefully.
4.RedwoodJS
RedwoodJS is an opinionated, full-stack framework for React that bundles together best-in-class technologies. It aims to scale from a simple side project to a startup-ready application by integrating React, GraphQL, and Prisma into a single, cohesive developer experience.

Key Features
- GraphQL API: Automatically generates a GraphQL API from your database schema.
- Cells Architecture: Manages data fetching, loading, and error states for individual components.
- Integrated Tooling: Includes a powerful CLI for generating pages, services, and components.
5.Blitz.js
Blitz.js is a full-stack React framework built on top of Next.js with a “zero-API” philosophy. It allows you to call server-side functions directly from your React components, eliminating the need to build a separate REST or GraphQL API. This approach aims to dramatically increase developer productivity.

Key features
- Zero-API Data Layer: Call server functions directly from your front end.
- Convention over Configuration: Provides a highly opinionated structure for rapid development.
- Built-in Authentication & Authorization: Comes with a pre-configured user management system.
6.Meteor.js
Meteor.js is a full-stack JavaScript framework for building real-time applications with a single codebase. It’s known for its live data updates, which automatically sync changes between the database and the client. While its popularity has waned, it remains a strong choice for real-time dashboards or chat applications.

Key features
- Real-time Data Sync: Provides real-time updates between the client and server.
- Isomorphic Code: Allows the same code to run on both the client and server.
- Integrated Build System: Simplifies the build and deployment process.
7.Adonis.js
AdonisJS is a Node.js framework inspired by Laravel. It provides a full-featured, batteries-included environment for building web applications and APIs. Its clear structure, comprehensive tooling, and focus on developer experience make it a solid choice for creating robust, maintainable backend systems in TypeScript.

Key features
- MVC Architecture: Follows the classic Model-View-Controller pattern.
- ORM and Database Migrations: Includes its own powerful ORM for database interactions.
- Built-in Security: Provides protection against common web vulnerabilities like CSRF and XSS.
8.Sails.js
Sails.js is a Node.js framework inspired by Ruby on Rails. It’s designed to streamline the creation of custom, enterprise-grade Node.js applications and APIs. It has a flexible MVC structure and out-of-the-box support for WebSockets, making it a good fit for real-time applications.

Key features
- Blueprint APIs: Automatically generates RESTful API endpoints for your models.
- Waterline ORM: Provides a data-agnostic ORM that works with many databases.
- WebSocket Integration: Features built-in support for real-time communication.
9.Full- Stack Django
Full-Stack Django is a robust, Python-based framework that comes with everything you need to build a full-fledged web application. It follows a “batteries-included” philosophy, providing built-in features for authentication, an ORM, and templating. It is well-suited for complex, data-driven applications.

Key features
- “Batteries-Included” Philosophy: Comes with a built-in ORM, admin panel, and authentication.
- MVT (Model-View-Template) Architecture: A structured and logical approach to web development.
- Django REST Framework: The standard for building powerful and scalable APIs with Django.
10.Mojolicious
Mojolicious is a real-time web framework for Perl. It’s known for its simplicity and lightweight nature, providing a clean, object-oriented API with no hidden magic. It’s a complete toolkit that includes a web server, a template engine, and support for WebSockets.

Key features
- Single-File Applications: Allows you to build simple apps in a single file.
- Full-Stack and Real-time: Supports both HTTP and WebSockets for dynamic applications.
- Built-in Tools: Includes a web server, template engine, and testing framework.
In the ever-evolving world of web development, choosing the right framework is the single most important decision you can make for your project’s success. While this list highlights some of the most widely used and powerful frameworks available, the best one is ultimately the one that aligns with your unique vision. Your final choice should always serve your project’s specific needs, whether that’s a blazing-fast user interface, robust server-side security, or a streamlined, all-in-one solution.
If you’re looking to bring a world-class digital product to life and require expert guidance, our team at Global Media Insight has been at the forefront of the digital revolution since 2001. We provide cutting-edge web development and SEO services in Dubai, the UAE, and across the wider Middle East.
7 Things to Check Before Choosing a Web Framework
By now, you might have decided on the best framework for your web application.
Chances are you are already familiar with the specific framework, and you are ready to begin the project.
But are you sure it is the most appropriate framework for you?
To help you finalize the perfect framework, here are five things to keep in mind.
1. Good Documentation
Most of the time, even a code written by yourself can seem difficult to understand when you come back after a few months.
However, while using frameworks, you are working with someone else’s code – so pick a framework with good documentation and training to utilize the framework to its complete potential.
2. Functionality
Choose a framework that fits your requirements rather than picking one for its popularity.
For example, you do not want a full-stack framework if you need only routing functionality.
First, understand your specific needs, then evaluate different options.
3. Consistency
Even though a framework cannot replace coding standards and internal policies, choosing a good one can help you maintain consistency – especially if your developers are working from different places.
4. Business Factors
Consider your business needs while finalizing a framework.
For example, if you are a small business trying to partner with a big company, you will go for the framework used by the larger organization.
So, bear in mind that there might be future risks in managing it.
5. Customization and Configuration
Developers should be able to modify the framework’s functionality to conform to the unique requirements and specifications of the project, ensuring that the framework is appropriate for the project and flexible enough to meet its specific requirements.
6. Licensing
Some frameworks have stringent licensing requirements, which may restrict how they can be used or distributed.
It’s crucial to pick a framework whose license complements the project’s aims and purposes.
7. Support
Make sure that the framework you choose has an active community for support.
Once you start using a framework, it’s an integral part of your web app.
So without support, you will have to maintain it yourself or rewrite the code.
Wrapping Up
It is important to choose a framework that matches the nature of your project.
For instance, server-side rendering, faster development and SEO would be your priority.
We believe this list of the best frontend and backend frameworks and their features will help you choose the best one.
Also, please note this is not an all-inclusive list – we have picked the ones we think as the best.
There are many more excellent frameworks in the market.
Global Media Insight has been at the forefront of the digital revolution since 2001. We offer world-class web development services to our clients across the Middle East and India. If you are looking for an agency to develop your website, contact us today.





